Commemorating its 61st anniversary on January 8, 2026, the Faculty of Psychology of Universitas Gadjah Mada adopts the theme “Psychology in Synergy Toward a Resilient and Prosperous Nation.” This spirit is not merely a slogan, but a tangible reflection embodied in a series of reputable international scientific publications produced by the academic community of the Faculty of Psychology UGM over the past year. We have compiled these publications as a “special gift” that highlights the Faculty’s contributions across three main pillars: global mental health, Indonesian local wisdom, and disaster resilience.
SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
The Faculty of Psychology at Universitas Gadjah Mada (UGM), through the Center for Public Mental Health (CPMH), has implemented a series of psychosocial support programs for communities affected by floods and landslides in Aceh. Supported by Emergency Disaster Response Community Service Funding for the Aceh, North Sumatra, and West Sumatra regions from the Directorate of Research and Community Service (DPPM) of the Ministry of Higher Education, Science, and Technology, the program is designed to address the urgent mental health recovery needs of survivors while strengthening long-term psychosocial support systems at the community and local government levels.
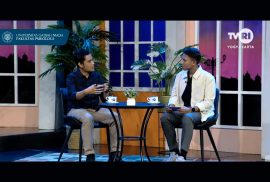
The Faculty of Psychology, Universitas Gadjah Mada, in collaboration with TVRI Yogyakarta, once again presents OPSI: Obrolan Psikologi (Psychology Talk) in its eighteenth episode, aired on Tuesday, 16 December 2025, from 15:00 to 16:00 WIB. This episode raises the theme “Mindful Spending at the End of the Year: When Emotions Control the Wallet.” It invites young people to become aware of emotional spending patterns, understand the triggers behind them, and build a healthier relationship with money through awareness, reflection, and personal values.
Universitas Gadjah Mada has once again conferred the Anugerah Insan Berprestasi (Outstanding Person Award) to members of its academic community and alumni who have demonstrated exceptional contributions and performance to the university and to society at large. This year, the Faculty of Psychology UGM is proud to receive the Inspiring Lecturer in Social Sciences and Humanities award, which is presented to faculty member IIndrayanti, S.Psi., M.Si., Ph.D., Psikolog.
Diana Setiyawati, S.Psi., MHSc., Ph.D., Psikolog, a lecturer at the Faculty of Psychology, Universitas Gadjah Mada (UGM), is one of the grantees of the Community Service Program for Emergency Disaster Response in the Provinces of Aceh, North Sumatra, and West Sumatra funded by the Directorate of Research and Community Service (DPPM), Ministry of Higher Education, Science, and Technology. She received funding for a program entitled “Integrated Psychosocial Recovery Program for Communities Affected by Floods in Sumatra.”
The Laboratory of Mental Processes and Behaviour (PMB), Faculty of Psychology, Universitas Gadjah Mada, held an international seminar titled “Studying Mental Processes Using EEG/ERP” on Friday (05/12). The event, attended by 40 participants, was conducted in a hybrid format—via Zoom Meeting and on-site in Room A-203 at the Faculty of Psychology UGM. This seminar served as a platform for knowledge sharing and scientific discussion on the use of EEG and ERP in studying human mental processes.
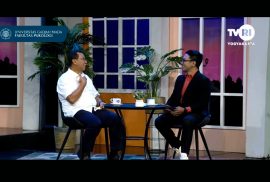
The Faculty of Psychology, Universitas Gadjah Mada, in collaboration with TVRI Yogyakarta, once again presents OPSI: Obrolan Psikologi (Psychology Talk) in its seventeenth episode, aired on Tuesday, 2 December 2025, from 15:00 to 16:00 WIB. This episode raises the theme “The Dilemma of Two Worlds: Work vs Family,” discussing the challenges faced by families in which both partners are working. The episode invites the public to understand the dynamics of roles and demands between the workplace and family life, as well as the importance of communication, fair division of roles, and emotional awareness in maintaining harmonious relationships.
The Faculty of Psychology, Universitas Gadjah Mada (UGM), in collaboration with Kesehatan Mental Tuli Indonesia (KMTI), organized a training titled “Bridging Minds: Mental Health Training for Deaf Leaders and Mental Health Professionals” on 20–21 November 2025 at the Faculty of Psychology UGM. This activity is part of a broader initiative to strengthen inclusive mental health support for Deaf communities in Indonesia.
The Faculty of Psychology at Universitas Gadjah Mada (UGM) held a series of activities titled Wellness Day: Maintaining Body and Mind in Harmony on Friday (14/10). The in-person event was attended by lecturers and administrative staff of the Faculty of Psychology.
The Center for Indigenous and Cultural Psychology (CICP) of the Faculty of Psychology, Universitas Gadjah Mada, participated in the u’GOOD Inaugural Conference titled “Thriving Together: Youth, Relational Wellbeing and the Future of the Global South,” held from October 7–9, 2025, in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. This inaugural conference served as the official launch of u’GOOD research projects across 9 Global South countries and marked the initial meeting of a Community of Practice (CoP) aimed at strengthening cross-national and interdisciplinary collaborations.